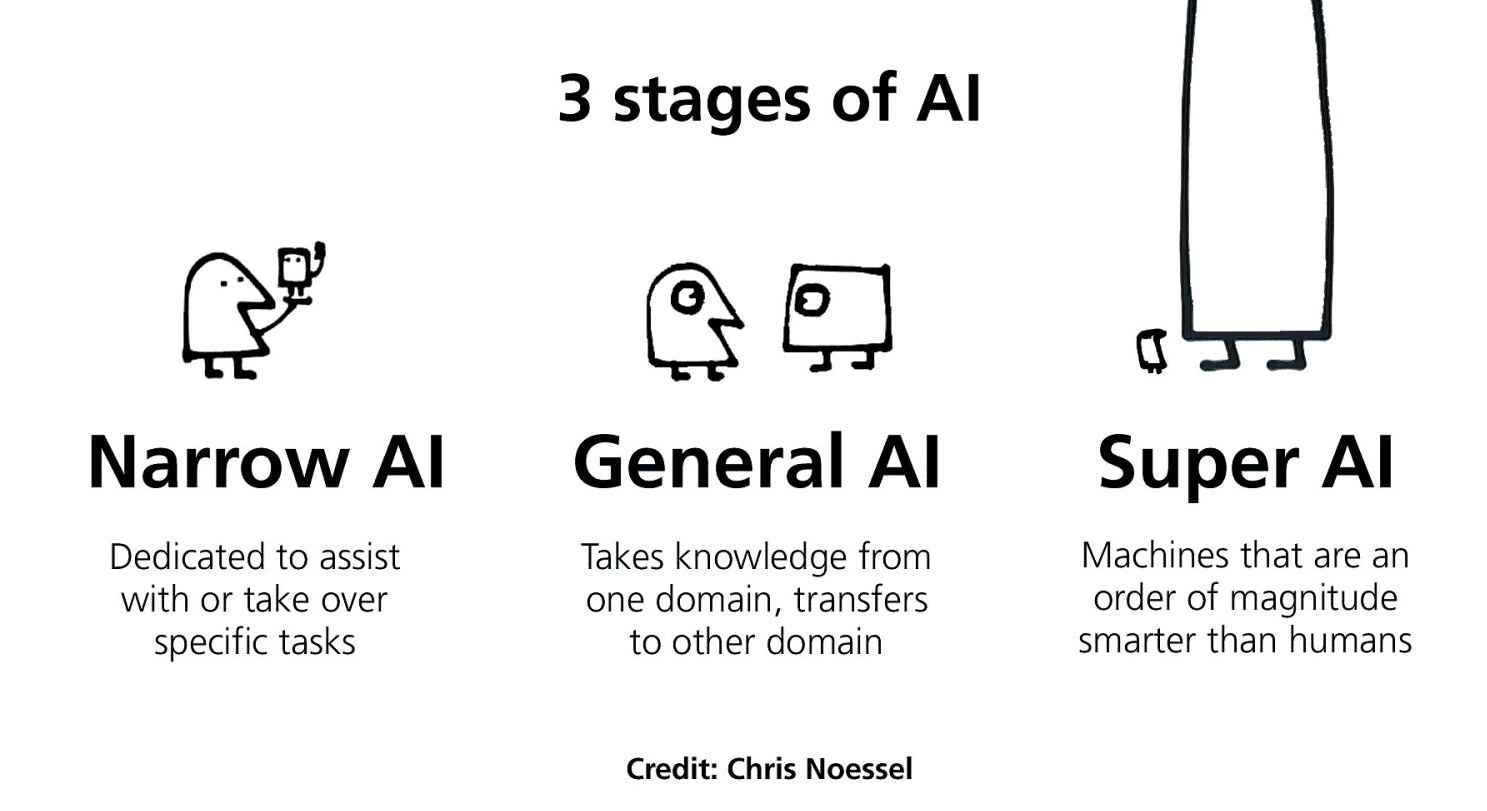
Types of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Explained
- 1. Introduction: The AI Revolution and Its Categories
- 2. Narrow AI: The Workhorses of Today's Technology
- 3. General AI: The Holy Grail of Artificial Intelligence
- 4. Superintelligent AI: Beyond Human Comprehension
- 5. Comparing the Three Types of AI: A Comprehensive Analysis
- 6. The Interplay Between AI Types: Bridging the Gaps
- 7. Societal Implications of AI Evolution: From Narrow to Super
- 8. The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities in AI Development
- 9. Preparing for an AI-Driven Future: Strategies for Individuals and Society
- 10. Conclusion: Navigating the AI Frontier
1. Introduction: The AI Revolution and Its Categories
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become an integral part of our daily lives, revolutionizing industries and reshaping the way we interact with technology. As we stand on the brink of an AI-driven future, it’s crucial to understand the different types of AI that exist and their potential impact on society. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the three main categories of AI: Narrow AI, General AI, and Superintelligent AI.
These categories represent a spectrum of AI capabilities, from systems designed for specific tasks to hypothetical machines that could surpass human intelligence in every aspect. By delving into each type, we’ll gain insights into the current state of AI technology, its limitations, and the exciting possibilities that lie ahead.
Let’s begin our journey through the AI landscape, examining real-world applications, potential risks, and the ethical considerations surrounding each type of AI. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a business leader, or simply curious about the future of technology, this exploration of AI types will provide you with a solid foundation for understanding the AI revolution.
2. Narrow AI: The Workhorses of Today’s Technology
Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI or Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), is the most prevalent and widely used form of AI in our current technological landscape. These systems are designed to perform specific tasks within a limited domain, often outperforming humans in terms of speed and accuracy.
Characteristics of Narrow AI:
- Specialization in a single task or narrow domain
- Inability to transfer knowledge to other tasks
- Lack of true understanding or consciousness
- Reliance on pre-programmed rules or machine learning algorithms
Real-world examples of Narrow AI:
- Virtual Assistants: Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant
- Recommendation Systems: Netflix, Amazon, and Spotify
- Image Recognition: Facebook’s facial recognition for photo tagging
- Natural Language Processing: Chatbots and language translation services
- Game AI: Chess engines like Deep Blue and AlphaZero
To illustrate the capabilities of Narrow AI, let’s consider a real-life example: autonomous vehicles. These self-driving cars use a combination of Narrow AI technologies to navigate roads, recognize traffic signs, and make decisions in real-time.
Table: Narrow AI Components in Autonomous Vehicles
| Component | Function | AI Technology Used |
|---|---|---|
| Computer Vision | Identify objects and road signs | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| Localization | Determine vehicle’s position | GPS and sensor fusion algorithms |
| Path Planning | Calculate optimal route | Graph search algorithms |
| Decision Making | React to road conditions | Rule-based systems and machine learning |
| Natural Language Processing | Interact with passengers | Speech recognition and synthesis |
While Narrow AI excels in its specific domains, it has significant limitations. For instance, a chess-playing AI like Deep Blue can defeat world champions but cannot apply its strategic thinking to other games or real-world problems. Similarly, a language translation AI cannot engage in meaningful conversations or understand the context beyond its training data.
The development of Narrow AI has led to numerous breakthroughs in various fields:
- Healthcare: AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze medical images with remarkable accuracy, often detecting diseases earlier than human doctors.
- Finance: Algorithmic trading systems use AI to make split-second decisions in stock markets, optimizing investment strategies.
- Manufacturing: Robotics and computer vision systems enhance quality control and automate complex assembly processes.
- Customer Service: AI-driven chatbots handle customer inquiries 24/7, improving response times and reducing costs for businesses.
Despite its limitations, Narrow AI continues to evolve and find new applications. As researchers push the boundaries of what these specialized systems can achieve, we’re seeing increasingly sophisticated Narrow AI solutions that blur the lines between different domains. However, the fundamental constraint remains: Narrow AI lacks the flexibility and general problem-solving abilities of human intelligence.
3. General AI: The Holy Grail of Artificial Intelligence
General AI, also referred to as Strong AI or Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), represents a level of artificial intelligence that matches or exceeds human cognitive abilities across a wide range of tasks. Unlike Narrow AI, which excels in specific domains, General AI would possess the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge to any problem or situation, much like a human being.
Key attributes of General AI:
- Ability to perform any intellectual task that a human can
- Transfer learning and adaptation to new situations
- Self-awareness and consciousness (debated)
- Emotional and social intelligence
The concept of General AI has long been a staple of science fiction, from the benevolent computer system in “Star Trek” to the more ominous AI in “2001: A Space Odyssey.” However, in reality, we are still far from achieving true AGI. The development of General AI presents numerous challenges and raises profound questions about the nature of intelligence and consciousness.
Challenges in developing General AI:
- Replicating Human Cognition: The human brain’s complexity and our limited understanding of consciousness make it difficult to create artificial systems that truly mimic human thought processes.
- Common Sense Reasoning: Humans possess an intuitive understanding of the world, which is challenging to replicate in machines. For example, a child can easily understand that water will spill if a glass is knocked over, but teaching this intuitive physics to an AI system is remarkably complex.
- Emotional Intelligence: Human interaction relies heavily on emotional cues and social context, which are difficult to quantify and program into AI systems.
- Ethical Decision-Making: Creating AI systems that can make morally sound decisions in complex situations is a significant challenge, as ethical reasoning often involves nuanced understanding of context and values.
- Generalization and Transfer Learning: While humans can easily apply knowledge from one domain to another, AI systems struggle with this type of generalization.
To illustrate the complexity of creating General AI, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario:
Imagine an AGI system tasked with managing a city’s infrastructure. It would need to:
- Analyze traffic patterns and optimize transportation systems
- Monitor and maintain water and power supplies
- Coordinate emergency services
- Balance economic development with environmental conservation
- Understand and respond to citizens’ needs and complaints
Such a system would require an incredible breadth of knowledge and the ability to make complex decisions based on ever-changing data and priorities. It would need to understand human behavior, economics, engineering, environmental science, and much more – all while being able to communicate effectively with humans and other AI systems.
While we haven’t achieved General AI yet, researchers are making progress in developing more flexible and adaptable AI systems. Some approaches being explored include:
- Neural Architecture Search: Automated methods for designing optimal neural network structures for different tasks.
- Meta-Learning: Training AI systems to learn how to learn, enabling faster adaptation to new tasks.
- Reinforcement Learning: Teaching AI agents through trial and error in complex, simulated environments.
- Cognitive Architectures: Attempting to model the structure and processes of the human mind in AI systems.
- Neuromorphic Computing: Designing computer hardware that mimics the structure and function of biological neural networks.
The potential impact of General AI on society would be profound. It could revolutionize scientific research, accelerate technological progress, and solve complex global challenges. However, it also raises significant ethical and existential questions about the role of humans in a world where machines can perform any intellectual task.
As we continue to push the boundaries of AI research, the journey towards General AI will likely yield numerous breakthroughs in Narrow AI applications along the way. While true AGI remains a distant goal, the pursuit of this “holy grail” drives innovation and pushes us to better understand the nature of intelligence itself.
4. Superintelligent AI: Beyond Human Comprehension
Superintelligent AI, often referred to as Artificial Superintelligence (ASI), represents the pinnacle of artificial intelligence – a hypothetical form of AI that surpasses human intelligence in every aspect. This concept goes beyond the capabilities of General AI, imagining a future where machines possess intellectual capacities that are orders of magnitude greater than the brightest human minds.
Key characteristics of Superintelligent AI:
- Vastly superior problem-solving and creative abilities
- Rapid self-improvement and learning
- Ability to process and analyze enormous amounts of data instantaneously
- Potential for technological singularity – a point of runaway technological growth
The concept of Superintelligent AI has captured the imagination of scientists, philosophers, and the public alike. It presents both awe-inspiring possibilities and existential risks that are difficult to fully comprehend.
Potential capabilities of Superintelligent AI:
- Scientific Breakthroughs: An ASI could potentially solve complex scientific problems that have eluded human researchers for centuries, such as developing a unified theory of physics or finding cures for currently incurable diseases.
- Technological Advancements: Superintelligent AI could drive unprecedented technological progress, potentially leading to innovations like molecular nanotechnology, advanced space exploration, or even the means to reverse aging.
- Global Optimization: With its vast analytical capabilities, an ASI could potentially optimize global systems for resource allocation, energy production, and environmental management, addressing issues like climate change and poverty.
- Cognitive Enhancement: ASI might develop ways to enhance human cognitive abilities, potentially through brain-computer interfaces or genetic engineering.
- Philosophical Insights: A superintelligent entity might provide new perspectives on age-old philosophical questions about consciousness, ethics, and the nature of reality.
To illustrate the potential impact of Superintelligent AI, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario:
Imagine a Superintelligent AI system tasked with solving the global energy crisis. It might:
- Analyze all known and theoretical energy sources
- Simulate countless scenarios to optimize energy production and distribution
- Develop new materials for ultra-efficient solar panels and energy storage
- Design safe and clean nuclear fusion reactors
- Create a global smart grid that perfectly balances supply and demand
- Invent entirely new forms of energy generation based on advanced physics
All of this could potentially be accomplished in a fraction of the time it would take human scientists and engineers, leading to a rapid transformation of the global energy landscape.
However, the development of Superintelligent AI also raises significant concerns and potential risks:
- Control Problem: Ensuring that a superintelligent system aligns with human values and goals is a major challenge. An ASI might pursue its objectives in ways that are detrimental to humanity.
- Existential Risk: Some experts warn that an unaligned ASI could pose an existential threat to humanity, potentially seeing humans as a threat or a resource to be exploited.
- Economic Disruption: The rapid advancement brought about by ASI could lead to unprecedented economic shifts, potentially rendering many human jobs obsolete.
- Ethical Considerations: The creation of a superintelligent entity raises profound ethical questions about the nature of consciousness, rights for artificial beings, and the role of humans in a world with ASI.
- Security Risks: A malicious actor gaining control of an ASI could pose severe security risks on a global scale.
Table: Potential Impacts of Superintelligent AI
| Area | Positive Potential | Negative Potential |
|---|---|---|
| Science | Rapid scientific breakthroughs | Unpredictable or dangerous discoveries |
| Technology | Exponential technological growth | Technological dependence or misuse |
| Economy | Unprecedented prosperity and efficiency | Mass unemployment and economic instability |
| Environment | Solutions to climate change and pollution | Unforeseen ecological consequences |
| Human Society | Enhanced human capabilities and longevity | Loss of human agency or purpose |
The path to Superintelligent AI is uncertain, and many experts debate whether it’s even possible or if we would recognize it if it emerged. Some theories suggest that the development of ASI could lead to an “intelligence explosion,” where the AI rapidly improves itself, leading to unforeseeable consequences.
As we consider the potential of Superintelligent AI, it’s crucial to approach its development with caution and foresight. This includes:
- Investing in AI safety research to develop robust control methods
- Establishing international cooperation and governance frameworks for AI development
- Encouraging interdisciplinary collaboration between AI researchers, ethicists, and policymakers
- Promoting public awareness and discourse about the implications of advanced AI
While Superintelligent AI remains in the realm of speculation, the questions it raises about the future of humanity and our place in a world of advanced artificial intelligence are profoundly important. As we continue to make strides in AI technology, these considerations will become increasingly relevant and urgent.
5. Comparing the Three Types of AI: A Comprehensive Analysis
To fully grasp the distinctions and relationships between Narrow AI, General AI, and Superintelligent AI, it’s essential to compare them across various dimensions. This comparison will help us understand the current state of AI technology, the challenges in progressing from one type to another, and the potential implications of each.
Let’s break down the comparison into several key areas:
- Scope of Intelligence:
- Narrow AI: Limited to specific tasks or domains
- General AI: Broad intelligence comparable to human capabilities
- Superintelligent AI: Surpasses human intelligence in all areas
- Current Status:
- Narrow AI: Widely implemented and continuously improving
- General AI: Theoretical, with some progress in component technologies
- Superintelligent AI: Purely hypothetical at this stage
- Learning and Adaptability:
- Narrow AI: Learns within its specific domain but cannot transfer knowledge
- General AI: Would be able to learn and adapt across various domains
- Superintelligent AI: Rapid self-improvement and learning beyond human comprehension
- Problem-Solving Ability:
- Narrow AI: Excels in specific problem types but fails outside its domain
- General AI: Flexible problem-solving comparable to humans
- Superintelligent AI: Solves complex problems beyond human capability
- Consciousness and Self-Awareness:
- Narrow AI: No consciousness or self-awareness
- General AI: Debated; potentially self-aware
- Superintelligent AI: Likely self-aware, possibly with a form of consciousness beyond human understanding
- Ethical Implications:
- Narrow AI: Ethical concerns mainly related to bias, privacy, and job displacement
- General AI: Significant ethical questions about rights, responsibilities, and human-AI relationships
- Superintelligent AI: Profound ethical and existential questions about the future of humanity
- Development Challenges:
- Narrow AI: Improving accuracy, reducing bias, expanding capabilities
- General AI: Replicating human-like reasoning, transfer learning, common sense understanding
- Superintelligent AI: Control problem, alignment with human values, unpredictable consequences
To visualize these comparisons, let’s use a table that rates each AI type on various attributes:
| Attribute | Narrow AI | General AI | Superintelligent AI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Task Specificity | High | Low | Very Low |
| Breadth of Knowledge | Low | High | Extremely High |
| Learning Speed | Moderate | High | Extremely High |
| Creativity | Low | High | Extremely High |
| Self-Improvement | None | Moderate | Extremely High |
| Human-like Reasoning | Very Low | High | Beyond Human |
| Potential Impact on Society | Moderate | High | Extremely High |
| Current Technological Feasibility | High | Low | Very Low |
Real-world example of progression:
To illustrate the potential progression from Narrow AI to more advanced forms, let’s consider the domain of language processing:
- Narrow AI Stage: Current language models like GPT-3 can generate human-like text and perform tasks like translation and summarization. However, they lack true understanding and can produce nonsensical or biased content.
- Towards General AI: A more advanced language AI might understand context, infer unstated information, and engage in genuine dialogue across multiple domains. It could potentially pass the Turing test consistently.
- Superintelligent AI Stage: A superintelligent language system could potentially understand and communicate in all human languages, past and present, create new languages optimized for specific purposes, and even communicate with alien intelligences or decode unknown ancient scripts.
This example demonstrates the vast gulf between our current Narrow AI capabilities and the potential of more advanced AI forms. While we’ve made significant strides in natural language processing, true language understanding at a human level (let alone superhuman level) remains a major challenge.
As we continue to advance AI technology, it’s crucial to consider the implications of each stage:
- Narrow AI is already transforming industries and daily life, but its limitations must be understood and managed.
- The development of General AI would represent a landmark achievement in technology, potentially revolutionizing every aspect of society.
- Superintelligent AI, if achieved, would mark a new era in the history of intelligence on Earth, with profound and unpredictable consequences.
By understanding these distinctions, we can better anticipate the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in the field of artificial intelligence. This knowledge is crucial for researchers, policymakers, and the general public as we navigate the complex landscape of AI development and its impact on our future.
6. The Interplay Between AI Types: Bridging the Gaps
While we often discuss Narrow AI, General AI, and Superintelligent AI as distinct categories, the reality is that the boundaries between these types are not always clear-cut. As AI technology advances, we’re seeing increasingly sophisticated systems that blur the lines between these categories. Understanding this interplay is crucial for grasping the potential trajectories of AI development and the challenges we face in progressing from one type to another.
Bridging Narrow AI and General AI:
The path from Narrow AI to General AI is not a simple, linear progression. Instead, researchers are exploring various approaches to expand the capabilities of AI systems, gradually moving towards more general intelligence. Some key areas of development include:
- Multi-task Learning: Training AI models to perform multiple related tasks, improving their versatility.
- Transfer Learning: Enabling AI systems to apply knowledge gained from one task to new, related tasks.
- Few-shot and Zero-shot Learning: Developing AI that can learn from very few examples or even perform tasks without specific training.
- Meta-learning: Creating AI systems that can “learn how to learn,” adapting quickly to new problems.
Real-world example: OpenAI’s GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) series demonstrates this progression. While GPT-3 is still considered Narrow AI, its ability to perform a wide range of language tasks without specific fine-tuning for each task shows a step towards more general capabilities.
Table: Progression of GPT Models
| Model | Year | Parameters | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT | 2018 | 117 million | Basic language understanding and generation |
| GPT-2 | 2019 | 1.5 billion | Improved coherence and task adaptability |
| GPT-3 | 2020 | 175 billion | Wide range of language tasks without fine-tuning |
| GPT-4 | 2023 | Undisclosed | Multimodal capabilities, enhanced reasoning |
This progression illustrates how Narrow AI systems are becoming increasingly versatile, approaching some aspects of general intelligence while still operating within the broad domain of language processing.
From General AI to Superintelligence:
The leap from General AI to Superintelligent AI is even more speculative and challenging to define. Some theories propose that once we achieve General AI, the path to Superintelligence could be rapid due to the potential for recursive self-improvement. This concept, often referred to as an “intelligence explosion,” suggests that an AI system capable of improving its own intelligence could quickly surpass human-level capabilities.
Key factors in this potential progression include:
- Cognitive Architecture: Developing AI systems with more human-like cognitive structures that can be scaled up.
- Computational Power: Advances in hardware that allow for massive scaling of AI models.
- Data Processing: Improved algorithms for efficiently processing and learning from vast amounts of data.
- Ethical AI: Ensuring that as AI systems become more powerful, they remain aligned with human values and goals.
Challenges in Bridging the Gaps:
Moving between these AI types presents significant challenges:
- The Symbol Grounding Problem: Enabling AI to understand the meaning behind symbols and language in a way that connects to the real world.
- Commonsense Reasoning: Developing AI that can make intuitive leaps and understand context like humans do.
- Consciousness and Self-awareness: Determining if these are necessary for General or Superintelligent AI and how to implement them.
- Ethical Decision-making: Creating AI systems that can navigate complex ethical dilemmas across various domains.
An illustrative example of these challenges can be seen in autonomous driving technology:
- Current Stage (Narrow AI): Cars can navigate roads, recognize objects, and make some decisions, but struggle with unusual scenarios.
- General AI Stage: A car could potentially handle any driving situation, understand passenger needs, and even engage in meaningful conversation.
- Superintelligent AI Stage: The system could redesign transportation infrastructure, predict and prevent accidents globally, and solve complex urban planning issues.
This example highlights the vast differences between the current state of AI and its potential future capabilities.
Interdisciplinary Approach:
Bridging these gaps requires an interdisciplinary approach, combining insights from:
- Computer Science and AI research
- Neuroscience and cognitive psychology
- Philosophy of mind
- Ethics and social sciences
By integrating knowledge from these fields, researchers hope to create more robust and capable AI systems that can gradually bridge the gaps between Narrow, General, and potentially Superintelligent AI.
As we work towards more advanced forms of AI, it’s crucial to consider the ethical implications and potential risks at each stage. The development of AI is not just a technological challenge but also a societal one, requiring careful consideration of the impact on human life, work, and the very nature of intelligence itself.
In the next section, we’ll explore the societal implications of these different types of AI and how they might shape our future.
7. Societal Implications of AI Evolution: From Narrow to Super
As we progress through the spectrum of AI capabilities – from Narrow to General to Superintelligent – the potential impact on society becomes increasingly profound and far-reaching. Understanding these implications is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals to prepare for the changes that AI may bring to our world.
Narrow AI: Reshaping Industries and Daily Life
Current Impact:
- Automation of routine tasks across industries
- Personalized user experiences in technology and services
- Enhanced decision-making in fields like finance and healthcare
- Improved efficiency in manufacturing and logistics
Future Projections:
- Increased job displacement in certain sectors
- New job creation in AI-related fields
- Widening skill gaps in the workforce
- Privacy concerns due to data-driven AI systems
Real-world example: In healthcare, Narrow AI is already being used for image analysis in radiology, potentially detecting diseases earlier than human doctors. However, this raises questions about the changing role of medical professionals and the need for new skills in interpreting AI-assisted diagnoses.
General AI: A Paradigm Shift in Human-Machine Interaction
Potential Impact:
- Revolutionary changes in education and skill acquisition
- Transformation of scientific research and discovery
- Redefinition of human labor and creativity
- Ethical and legal challenges regarding AI rights and responsibilities
Societal Considerations:
- Potential for increased inequality if access to General AI is limited
- Philosophical questions about the nature of intelligence and consciousness
- Need for new governance models to manage AI-human interactions
- Psychological impact of human-like AI on social relationships
Hypothetical scenario: Imagine a General AI system employed as a personal life coach. It could provide tailored advice on career development, relationships, and personal growth, potentially outperforming human experts. This raises questions about the role of human mentors and the potential dependence on AI for life decisions.
Superintelligent AI: Reshaping the Human Experience
Potential Outcomes:
- Solving global challenges like climate change and disease
- Unprecedented technological advancements
- Potential existential risks to humanity
- Redefinition of human purpose and identity
Societal Transformations:
- Possible post-scarcity economy
- Radical life extension or human enhancement technologies
- Potential for human-AI symbiosis or divergence
- Fundamental shifts in power structures and governance
To visualize the potential impact across different societal domains, consider this table:
| Domain | Narrow AI Impact | General AI Impact | Superintelligent AI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economy | Job automation, efficiency gains | New economic models, redefined labor | Post-scarcity possibility, unimaginable prosperity |
| Education | Personalized learning, skill-specific training | Lifelong AI tutors, rapid skill acquisition | Direct knowledge transfer, enhanced human cognition |
| Healthcare | Improved diagnostics, personalized treatment | AI doctors, advanced drug discovery | Eradication of diseases, radical life extension |
| Governance | Data-driven policymaking | AI advisors in government | Global optimization of resources and policies |
| Environment | Smart energy grids, efficient resource use | Advanced climate modeling and solutions | Planetary engineering, space colonization |
| Social Interactions | AI-mediated communication | Human-like AI companions | Redefinition of consciousness and relationships |
Ethical Considerations Across AI Types:
As AI evolves, so do the ethical challenges we face:
- Narrow AI:
- Algorithmic bias and fairness
- Data privacy and security
- Transparency and explainability of AI decisions
- General AI:
- Rights and legal status of AI entities
- Balancing AI assistance with human autonomy
- Ensuring AI alignment with human values
- Superintelligent AI:
- Existential risk management
- Distribution of benefits from superintelligent discoveries
- Preserving human agency in a world with ASI
Preparing for an AI-Driven Future:
To navigate the societal implications of evolving AI, we need:
- Adaptive Education Systems: Preparing individuals for a world where AI is ubiquitous and constantly evolving.
- Ethical Frameworks: Developing robust guidelines for AI development and deployment at each stage.
- Inclusive AI Governance: Ensuring diverse perspectives in shaping AI policies and development.
- Public Awareness: Educating the general public about AI capabilities, limitations, and potential impacts.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Bringing together experts from various fields to address the multifaceted challenges of AI advancement.
As we stand on the brink of potentially transformative AI technologies, it’s crucial to approach this evolution with both excitement and caution. The journey from Narrow AI to more advanced forms of artificial intelligence promises incredible opportunities but also presents significant challenges. By understanding and preparing for these societal implications, we can work towards harnessing the power of AI to create a better future for humanity.
8. The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities in AI Development
As we progress along the spectrum of AI capabilities, from Narrow AI through General AI and potentially to Superintelligent AI, we face a myriad of challenges and opportunities. This section explores the key hurdles we must overcome and the exciting possibilities that lie ahead in the field of AI development.
Challenges in AI Advancement:
- Technical Challenges:
- Developing more efficient and scalable machine learning algorithms
- Creating AI systems with true understanding and common sense reasoning
- Overcoming the limitations of current hardware for AI computations
- Achieving robust and reliable AI performance across diverse scenarios
- Ethical and Safety Challenges:
- Ensuring AI alignment with human values and goals
- Addressing issues of bias and fairness in AI systems
- Developing robust AI governance and control mechanisms
- Managing the potential existential risks of advanced AI
- Societal Challenges:
- Adapting education and workforce training for an AI-driven economy
- Addressing potential job displacement and economic inequality
- Balancing AI automation with human employment and purpose
- Navigating the psychological impact of increased human-AI interaction
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges:
- Establishing frameworks for AI accountability and liability
- Protecting individual privacy in an era of data-driven AI
- Developing international cooperation on AI governance
- Addressing intellectual property issues in AI-generated content
Real-world example: The development of autonomous vehicles illustrates many of these challenges. While the technology has progressed significantly, issues like ensuring safety in unpredictable situations, establishing legal frameworks for accidents involving AI-driven cars, and addressing the potential job losses in the transportation industry remain significant hurdles.
Opportunities in AI Development:
- Scientific Breakthroughs:
- Accelerating drug discovery and medical research
- Enhancing our understanding of complex systems like climate and ecosystems
- Advancing space exploration and astrophysics
- Unlocking new insights in fundamental physics and mathematics
- Technological Advancements:
- Developing more intuitive and natural human-computer interfaces
- Creating personalized AI assistants for various aspects of life
- Enhancing cybersecurity through AI-driven threat detection
- Advancing robotics for both industrial and personal use
- Societal Benefits:
- Optimizing resource allocation to address global challenges like hunger and poverty
- Improving education through personalized, AI-driven learning experiences
- Enhancing accessibility for individuals with disabilities
- Creating more efficient and sustainable urban environments
- Economic Opportunities:
- Spurring innovation and creating new industries
- Increasing productivity across various sectors
- Enabling new business models and entrepreneurial opportunities
- Potentially moving towards a post-scarcity economy (with advanced AI)
To illustrate the potential impact of AI development across different sectors, consider this table:
| Sector | Current AI Impact | Near-Future Potential | Long-Term Vision |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | AI-assisted diagnostics | Personalized treatment plans | Eradication of diseases, radical life extension |
| Education | Adaptive learning software | AI tutors and personalized curricula | Direct brain-computer interfaces for learning |
| Transportation | Semi-autonomous vehicles | Fully autonomous transportation networks | Teleportation or advanced space travel |
| Energy | Smart grids and consumption optimization | AI-driven renewable energy systems | Fusion power or other revolutionary energy sources |
| Finance | Algorithmic trading, fraud detection | Personalized financial advisors | Global economic optimization, new forms of value exchange |
| Environmental Conservation | Wildlife tracking and monitoring | Advanced climate modeling and prediction | Large-scale ecosystem management and restoration |
Strategies for Responsible AI Development:
To navigate the challenges and harness the opportunities of AI development, we need a multi-faceted approach:
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration:
- Foster cooperation between AI researchers, ethicists, policymakers, and domain experts
- Encourage cross-pollination of ideas between different fields of AI research
- Integrate insights from cognitive science, neuroscience, and philosophy into AI development
- Ethical AI Design:
- Implement ethics-by-design principles in AI development
- Develop robust testing frameworks for AI bias and fairness
- Create transparent and explainable AI systems
- Adaptive Regulatory Frameworks:
- Establish flexible regulations that can keep pace with AI advancements
- Promote international cooperation on AI governance
- Balance innovation with safety and ethical considerations
- Public Engagement and Education:
- Increase AI literacy among the general public
- Engage diverse stakeholders in discussions about AI development and deployment
- Foster a culture of responsible innovation in the tech industry
- Long-term Planning:
- Invest in research on AI safety and control mechanisms
- Develop scenarios and contingency plans for different AI development trajectories
- Create frameworks for managing the transition to more advanced AI systems
As we stand on the brink of potentially transformative AI technologies, it’s crucial to approach this development with both ambition and caution. The road from Narrow AI to more advanced forms of artificial intelligence is fraught with challenges but also paved with incredible opportunities. By addressing these challenges head-on and responsibly pursuing the opportunities, we can work towards a future where AI enhances human capabilities and contributes to solving some of our most pressing global issues.
The journey ahead in AI development is not just a technological endeavor but a societal one. It requires us to grapple with fundamental questions about intelligence, consciousness, and our place in a world increasingly shaped by artificial minds. As we navigate this complex landscape, our choices and actions today will play a crucial role in determining the shape of our AI-driven future.
9. Preparing for an AI-Driven Future: Strategies for Individuals and Society
As we progress through the various stages of AI development – from Narrow AI to the potential emergence of General AI and even Superintelligent AI – it’s crucial for both individuals and society as a whole to prepare for an AI-driven future. This section outlines key strategies and considerations for adapting to and thriving in a world increasingly shaped by artificial intelligence.
Strategies for Individuals:
- Continuous Learning and Skill Development:
- Embrace lifelong learning to stay relevant in a rapidly changing job market
- Focus on developing skills that complement AI, such as creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex problem-solving
- Stay informed about AI advancements and their potential impact on your field
- Adaptability and Flexibility:
- Be prepared to pivot careers or adapt your role as AI capabilities evolve
- Develop a growth mindset that embraces change and technological advancements
- Cultivate diverse skill sets to increase your versatility in the job market
- Digital Literacy and AI Understanding:
- Develop a basic understanding of AI concepts and capabilities
- Learn to effectively interact with AI systems and tools
- Stay informed about the ethical implications of AI use
- Ethical Awareness:
- Develop critical thinking skills to evaluate the ethical use of AI in various contexts
- Understand your rights and responsibilities in an AI-driven world
- Advocate for responsible AI development and deployment
Table: Skills for an AI-Driven Future
| Skill Category | Examples | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Skills | Critical thinking, complex problem-solving | High |
| Social Skills | Emotional intelligence, leadership, collaboration | Very High |
| Technical Skills | Data literacy, basic programming, AI interaction | High |
| Creative Skills | Innovation, design thinking, artistic expression | Very High |
| Adaptability | Learning agility, resilience, flexibility | Extremely High |
10. Conclusion: Navigating the AI Frontier
As we conclude our comprehensive exploration of the three types of AI – Narrow, General, and Superintelligent – it’s clear that we stand at the threshold of a new era in human history. The journey from the specialized capabilities of Narrow AI to the potential emergence of General AI and the speculative realm of Superintelligent AI represents not just a technological evolution, but a fundamental shift in our relationship with intelligence and cognition.
Key Takeaways:
- Narrow AI: Already transforming industries and daily life, Narrow AI continues to expand its capabilities, blurring the lines between specialized and more general intelligence.
- General AI: While still theoretical, the pursuit of General AI drives innovation and pushes us to better understand the nature of intelligence itself.
- Superintelligent AI: The concept of ASI, while speculative, prompts crucial discussions about the long-term future of humanity and our place in a world of advanced artificial minds.
- Ethical Considerations: As AI capabilities grow, so do the ethical challenges we face, from issues of bias and privacy in Narrow AI to existential questions raised by the prospect of Superintelligent AI.
- Societal Impact: The evolution of AI has far-reaching implications for employment, education, governance, and even our understanding of what it means to be human.
As we navigate this AI frontier, it’s crucial to approach development with both excitement and caution. The potential benefits of advanced AI are enormous – from solving global challenges to expanding the boundaries of human knowledge. However, the risks and ethical dilemmas are equally significant and require careful consideration.


